October 21, 2021 linux kubernetes beginner
Ingress on Kubernetes with Cert-Manager
Let’s start with the obvious question, What is an Ingress Controller?
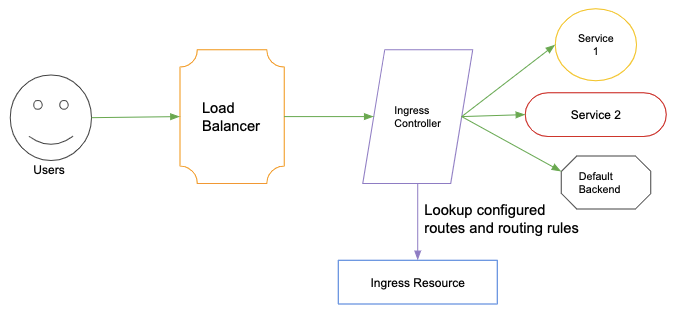
Ingress Controller is essentially a reverse proxy that is used to expose your service externally. It can be nginx, traefik, ambassador, HA proxy or any other piece of a custom web server that you have written yourself. All it does is it connects to the ingress resource in Kubernetes API which is listening on the specified address and routes the incoming traffic to the configured service accordingly. It works as Layer 7 (HTTP) load balancer compared to (Load Balancer type) Services which works as a Layer 4 (TCP/UDP over IP) Load Balancer.
How does Kubernetes Ingress works?
Kubernetes Ingress has two components i.e The Ingress resource and The Ingress controller. The Ingress resource is responsible for managing all the routing rules for the incoming traffic, and SSL termination. On the other hand, the Ingress Controller is the one that receives all the incoming traffic for a specified domain and with the help of the Ingress resource it implements the specified configuration. Such as SSL termination for a particular domain, routing traffic to the respective services, etc. E.g.:
A very common confusion can be around the usage of Ingress as compared to Services because from the first look it seems that everything that Ingress provides can be achieved via Services too. Therefore let’s try to compare them side-by-side:
| Services | Ingress |
|---|---|
| Limited to pre-defined “types” | Control loop that manages ingress |
| Obsolete “round-robin” based Load Balancing | Various Load Balancing strategies can be used depending on the controller |
| Dependent on your Kubernetes Master | Runs separately from your Kubernetes master |
| Tightly couples your application with the routing/networking rules i.e 1:1 mapping | Completely decoupled i.e your controller, routing rules and application are totally separate entities i.e 1:N mapping |
| Only one Load Balancer can be used per service when exposing it for external access | Single Load Balancer can be used to manage multiple domains. |
Understanding Ingress resource
The Ingress resource supports various rule configurations depending on your needs listed as below:
-
Self Signed or Local provided SSL certificates
-
SSL certificates from Let’s Encrypt using Cert-Manager
-
Virtual Host Routing
-
Path Based Routing
-
Custom Rules
Based on your requirement you can use Ingress in one of the following ways:
Example local SSL manifest:
apiVersion: v1
data:
tls.crt: base64 encoded cert
tls.key: base64 encoded key
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: testsecret
namespace: default
type: Opaque
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: no-rules-map
spec:
tls:
- secretName: testsecret
backend:
serviceName: s1
servicePort: 80
Example virtual host routing manifest:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test
spec:
rules:
- host: foo.bar.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: s1
servicePort: 80
- host: bar.foo.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: s2
servicePort: 80
Example path routing manifest:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- host: foo.bar.com
http:
paths:
- path: /foo
backend:
serviceName: s1
servicePort: 80
- path: /bar
backend:
serviceName: s2
servicePort: 80
Deploying an Ingress resource and Nginx Ingress controller for access over HTTP.
Here we will be deploying the Kubernetes Guestbook application and will make the application accessible via the URL http://ingress.aru.sh using Ingress.
-
We have pre-configured our URL’s nameserver to point to a Load Balancer which already has the respective Kubernetes instances attached to it.
-
Create an Nginx Ingress controller:
-
First deploy the mandatory manifest:
kubectl apply -fhttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/mandatory.yaml -
Depending on your Kubernetes cluster choose an installation method: GKE, Azure, BareMetal, Docker for Mac:
kubectl apply -fhttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/provider/cloud-generic.yaml -
Minikube:
minikube addons enable ingress -
For AWS visit: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/
-
-
Deploy the Kubernetes Guestbook application using the all-in-one manifest:
kubectl apply -fhttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/examples/master/guestbook/all-in-one/guestbook-all-in-one.yaml-n test-cert-manager-namespace -
Create an Ingress resource:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test-cert-manager-ingress namespace: test-cert-manager-namespace spec: rules: - host: ingress.aru.sh http: paths: - backend: serviceName: frontend servicePort: 80 -
Now you can access the freshly deployed Guestbook application on http://ingress.aru.sh.
Deploying an Ingress resource and Nginx Ingress controller for access over HTTPS.
Now we will be deploying the very same Kubernetes Guestbook application but this time we will make the application accessible over HTTPS at the URL http://ingress.aru.sh using SSL termination by Ingress and we will use cert-manager to automatically get a SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt using Ingress.
-
You can either deploy cert-manager in your cluster using Helm(link) or by using the static manifests(link).Do make sure to setup RBAC according to your cluster and your needs.
-
Create a cert-manager Issuer:
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Issuer metadata: name: test-cert-manager-issuer namespace: test-cert-manager-namespace spec: acme: email: <Your-Email-Addess> http01: {} privateKeySecretRef: key: "" name: test-cert-manager-secret server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directoryThe issuer will be responsible for connecting to the Let’s Encrypt ACME servers and getting the respective certificate based on the certificate request generated by the cert-manager Certificate resource.
Note: The created Issuer will only be valid for the specified namespace, if you want an Issuer that can be used throughout the cluster change kind: Issuer to kind: ClusterIssuer.
-
Create a cert-manager Certificate:
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Certificate metadata: name: test-cert-manager-certificate namespace: test-cert-manager-namespace spec: acme: config: - domains: - cert-manager.aru.sh http01: ingress: "" dnsNames: - cert-manager.aru.sh issuerRef: kind: Issuer name: test-cert-manager-issuer secretName: test-cert-manager-secret -
Alternatively, you can modify the previously created test-cert-manager-ingress Ingress resource to include an annotation to the cert-manager Issuer which will be read by the cert-manager ingress-shim and a respective Certificate resource will be created automatically for you:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test-cert-manager-ingress namespace: test-cert-manager-namespace annotations: certmanager.k8s.io/issuer: test-cert-manager-issuer spec: rules: - host: cert-manager.aru.sh http: paths: - backend: serviceName: test-cert-manager-service servicePort: 80 tls: - hosts: - cert-manager.aru.sh secretName: test-cert-manager-certificate -
Wait for few minutes for the cert-manager to get a new certificate from Let’s Encrypt and then you can access the deployed Kubernetes Guestbook application at https://ingress.aru.sh.
NOTE: We have used the Let’s Encrypt Staging ACME server in our example here. Therefore you will get an SSL warning when accessing the application over HTTPS. In real case scenario, you would want to use the “Let’s Encrypt Production ACME server” to get a production ready and signed SSL certificate. You will have to modify your cert-manager Issuer as below: server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory